The hum of a traditional gas generator has long been the soundtrack to power outages, camping trips, and job sites. But there's a quieter, cleaner revolution happening: the rise of solar generators. Imagine harnessing the sun's abundant energy to power your devices, keep your fridge cold, or even run essential home circuits—all without a drop of fossil fuel, obnoxious noise, or hazardous fumes. That's the promise of a solar generator, and understanding its basics and how they work can empower you to make a smarter energy choice for your life.
These innovative portable power solutions are far more than glorified battery packs; they represent a significant leap towards sustainable, on-demand electricity. Whether you're planning your next off-grid adventure or seeking reliable home backup, a deeper dive into these systems reveals just how accessible and powerful solar-powered energy has become.
At a Glance: Key Takeaways
- What it is: A portable power system combining solar panels and a battery to capture, store, and deliver clean electricity.
- Not a "generator": More accurately, a solar-powered battery system or portable power station with solar charging capabilities.
- How it works: Solar panels convert sunlight to DC, a charge controller regulates it, batteries store it, and an inverter converts it to AC for appliances.
- Key Benefits: Silent operation, zero emissions, no fuel costs, minimal maintenance, and multiple charging options.
- Main Limitation: Weather dependency for solar charging and slower "refueling" compared to gas.
- Common Uses: Camping, RVs, home backup during outages, remote work, emergency preparedness.
- Best Battery Type (2025): Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) for safety, longevity, and performance.
Demystifying the Solar Generator: More Than Just a Box
At its core, a solar generator is a self-contained portable power system designed to capture energy from the sun, store it, and then deliver it to your devices and appliances as needed. Unlike their noisy, fume-spewing cousins that burn gasoline, diesel, or propane, solar generators operate on a simple, elegant principle: converting sunlight into usable electricity.
While commonly called "generators," this term can be a bit misleading. Traditional generators generate power by converting fuel into mechanical energy, which then turns an alternator. Solar generators, however, don't generate power in this way. Instead, they act as sophisticated energy storage units that are charged by solar panels. Think of them as high-capacity, rechargeable battery banks that come with built-in charging intelligence and an array of power outlets. They are, perhaps, more accurately described as "solar-powered battery systems" or "portable power stations with solar charging capabilities."
These modern marvels are capable of powering everything from small electronics like smartphones and laptops to larger appliances such as refrigerators, power tools, and even some air conditioning units. And while direct sunlight is optimal for charging, most contemporary models offer versatile charging options, including standard wall outlets and car chargers, making them incredibly adaptable.
Understanding the Spectrum: Types of Solar Generators
Just as you wouldn't use a golf cart for a cross-country road trip, you wouldn't pick a small solar generator to power your entire home indefinitely. Solar generators come in various sizes and capacities, each designed for specific use cases. Understanding these categories is the first step in choosing the right system for your needs.
Portable Solar Generators (The Adventurer's Friend)
- Capacity: Typically 100Wh to 2000Wh
- Output: 100W to 2000W
- Best For: These compact units are perfect for adventurers, campers, RV enthusiasts, tailgaters, and anyone needing reliable power for essential devices on the go. They can easily charge phones, tablets, laptops, run portable fridges, LED lights, and small kitchen appliances like blenders. Their lightweight and often rugged design makes them truly portable.
Home Backup Solar Generators (The Guardian of Essentials)
- Capacity: Ranges from 2000Wh to 6000Wh
- Output: 2000W to 7200W
- Best For: Stepping up in power, these generators are designed to handle more significant loads during extended outages. They can reliably power multiple essential home appliances, keeping your refrigerator running for 1-3 days, ensuring your communication systems stay online, powering medical devices like CPAP machines, and illuminating crucial rooms. Many models in this range offer expandable battery options.
Whole-Home Solar Generator Systems (The Ultimate Resilience)
- Capacity: Starting at 10kWh and often exceeding 25kWh
- Output: Exceeding 10kW
- Best For: This category often involves more professional-grade installations, integrating directly into your home's electrical panel via an automatic transfer switch. These robust systems are built for long-duration, high-demand backup, capable of powering nearly an entire household for days, or even weeks, depending on solar input and usage. They are typically expandable and represent a serious investment in energy independence.
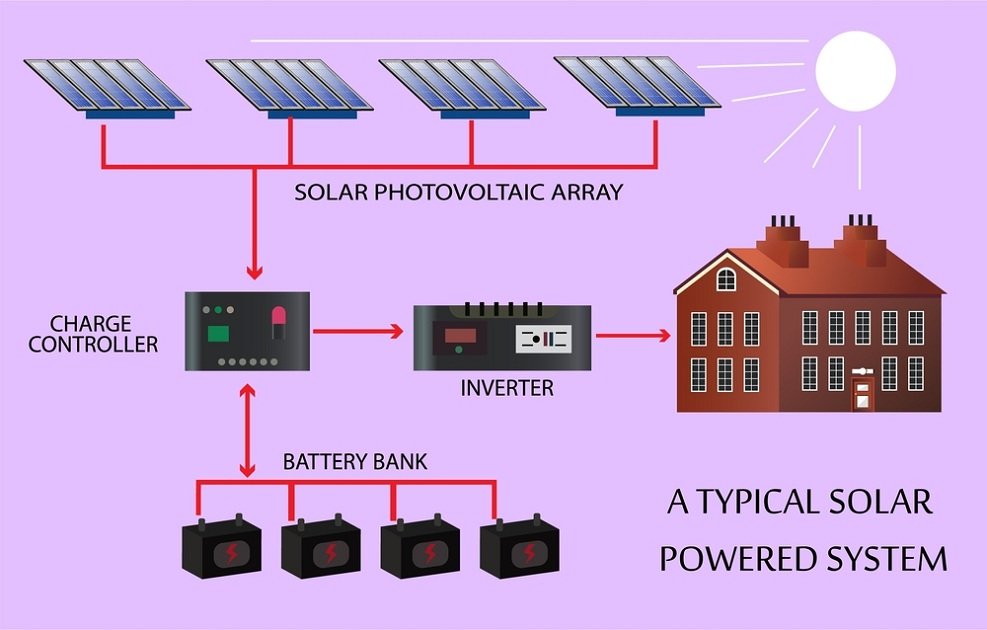
The Inner Workings: How Solar Generators Convert Light to Power
It might seem like magic, but the process of converting sunlight into usable electricity with a solar generator is a marvel of engineering, broken down into four key steps. Think of it as a carefully orchestrated relay race for electrons.
- Solar Energy Capture: The Panels Do the Heavy Lifting
It all begins with the solar panels—the unsung heroes of the system. These panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells. When sunlight (composed of tiny packets of energy called photons) hits these cells, it excites the electrons within them, causing them to flow and generate direct current (DC) electricity. This phenomenon is known as the photovoltaic effect. The more intense the sunlight, the more photons hit the panels, and the more electricity is produced. This is also where you might explore how to choose the right solar panels for optimal performance. - Power Regulation: Protecting Your Battery's Lifespan
The DC electricity coming directly from the solar panels can be erratic, fluctuating with sunlight intensity. If this unregulated power were sent straight to the battery, it could damage it, reduce its lifespan, or even pose a safety risk. This is where the charge controller steps in.
Modern solar generators almost exclusively use Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controllers. An MPPT controller constantly monitors the voltage and current from the solar panels and adjusts them to ensure the battery receives the optimal charge. It's like a smart traffic cop, directing the flow of electricity efficiently. MPPT controllers are significantly more efficient—typically 5-30% more so—than older Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controllers, maximizing the amount of energy harvested from your panels. - Energy Storage: The Heart of the System
Once the DC power is regulated, it's directed to the internal battery system for storage. This battery is the "fuel tank" of your solar generator. The vast majority of modern solar generators utilize advanced lithium-ion (Li-ion) or, increasingly, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries. These battery chemistries offer a superior balance of energy density, lifespan, and performance compared to older lead-acid options. The stored DC power waits patiently until you need to draw on it. - Power Conversion and Output: Ready for Your Devices
Most of the appliances and devices we use daily—from lamps to laptops to refrigerators—run on alternating current (AC) electricity. However, the power stored in the battery is direct current (DC). This creates a need for conversion, which is handled by a crucial component called the inverter.
The inverter's job is to efficiently convert the stored DC electricity into AC electricity, making it compatible with standard household outlets. Modern solar generators offer a variety of output options to cater to diverse needs:
- Standard AC Outlets: Typically 120V (or 240V on larger systems) for home appliances.
- USB Ports: 5V DC for charging smartphones, tablets, and other small electronics.
- 12V DC Outlets: Like a car's cigarette lighter port, useful for portable fridges or specialized DC devices.
- Wireless Charging Pads: Found on some advanced models for ultimate convenience.
This four-step process ensures that the sun's energy is efficiently captured, safely stored, and readily available in the format your devices need.
Solar Generator vs. Gas Generator: A Head-to-Head Battle
For years, gas generators were the undisputed champions of portable power. But with growing environmental concerns, rising fuel costs, and advancements in battery technology, solar generators are rapidly gaining ground. Let's pit them against each other to see how they stack up. This comparison will help you see why a complete guide to solar power generators is becoming an increasingly relevant resource.
| Feature | Solar Generator | Gas Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Cost | Free sunlight (once panels are purchased) | $3-5 per gallon (plus storage, stabilizers) |
| Noise Level | Silent (0 decibels) | Loud (50-80 decibels, like a vacuum cleaner or louder) |
| Maintenance | Minimal (clean panels, monthly charge, annual checks) | Regular oil changes, spark plug checks, tune-ups, fuel system upkeep |
| Indoor Use | Safe (zero emissions, no carbon monoxide risk) | Dangerous (carbon monoxide risk, outdoor use only) |
| Runtime | Limited by battery capacity and solar input (recharges) | Continuous as long as fuel is supplied |
| Initial Cost | $500-$6000+ (for generator + panels) | $300-$3000+ (for generator only) |
| Emissions | Zero operating emissions | CO2, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter |
| Weight | Often lighter for comparable power (due to LiFePO4) | Heavy due to engine, fuel tank, and frame |
The Real Cost: Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Value
At first glance, the price tag of a solar generator might seem higher than a comparable gas model. However, this is a classic example of looking beyond the upfront cost to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO) and return on investment (ROI).
While a gas generator might cost $300-$1000 initially, you'll be pouring money into fuel every time you run it. For example, a mid-sized gas generator might consume 1 gallon of gas every 4-8 hours. If used just 100 hours a year, that's 12-25 gallons, costing $36-$125 annually, plus oil changes and other maintenance. Over 10 years, these costs add up dramatically, potentially exceeding $6,800 or more, including fuel and maintenance.
A comparable solar generator system (generator + panels) might cost $1,000-$3,000 upfront. But after that initial purchase, your "fuel" is free sunlight. Maintenance is minimal—a quick wipe down of the panels, maybe a monthly charge if unused. This means that over a 10-year period, the total cost for a solar generator could be around $1,950 (initial purchase plus very minor maintenance).
The Verdict on ROI: Solar generators typically pay for themselves within 3-5 years through fuel savings, significantly reduced maintenance, and the added benefits of silent, clean operation. The global solar generator market is expected to more than double from $596.5 million in 2025 to $1.32 billion by 2037, signaling a clear trend towards their long-term economic viability.
Beyond the Savings: Unpacking the Benefits of Solar Generators
The financial argument is compelling, but the advantages of solar generators extend far beyond your wallet. They offer a host of benefits that enhance convenience, safety, and environmental responsibility.
- Environmental Stewardship: Perhaps the most significant advantage is their eco-friendliness. Solar generators produce zero operating emissions. By choosing solar over gas, you prevent approximately 1,700 pounds of CO2 annually per 2000Wh unit, making a tangible difference in reducing your carbon footprint. It’s a clean energy solution for a cleaner planet.
- Cost Savings Over Time: As discussed, the initial investment pays off. No more trips to the gas station for generator fuel, no more worrying about fuel storage or spoilage. Your energy source is limitless and free. Minimal moving parts also mean fewer breakdowns and significantly lower maintenance costs compared to internal combustion engines.
- Unrivaled Portability & Convenience: Modern solar generators are designed with the user in mind. Many feature integrated wheels, telescoping handles, and compact, robust designs. The use of advanced lithium batteries makes them surprisingly lightweight for their power output, making them easy to move from the garage to the campsite or from room to room during an outage. For an even broader perspective on these flexible power solutions, check out our comprehensive guide to portable power stations.
- Whisper-Quiet Operation: Imagine running your essential appliances without the constant drone. Solar generators operate in complete silence (0 decibels), which is a huge advantage for residential areas, campsites, RV parks, or any scenario where noise pollution is a concern. You can even use them safely indoors without disturbing your neighbors or your peace and quiet.
- Versatile Charging Options: While solar panels are the primary (and free) charging method, these units are incredibly flexible. You can rapidly charge them from a standard AC wall outlet, often taking just 1-8 hours for a full charge. For on-the-go charging, most also connect to your vehicle's 12V car charger, taking a bit longer (6-12 hours). Some advanced models even allow charging from traditional gas generators (though this defeats the "zero emissions" benefit during charging).
The Other Side of the Coin: Limitations and Considerations
While solar generators offer compelling advantages, they are not without their limitations. Understanding these potential drawbacks is crucial for setting realistic expectations and making an informed decision.
- Weather Dependency: The efficiency of solar charging is directly tied to the sun. In direct, clear sunlight, panels operate at close to 100% efficiency. However, in partial clouds, efficiency drops to 50-80%, and in heavy clouds, it can be as low as 10-25%. Rain and snow can significantly reduce or even block solar collection. This means your charging capabilities can vary greatly day by day.
- Charging Time: Unlike refueling a gas generator in minutes, fully charging a solar generator from panels takes time. Small units (around 500Wh) might take 3-6 hours in optimal sun, medium units (1500Wh) 6-12 hours, and large units (3000Wh+) 8-16 hours or more. While AC wall charging is much faster, relying solely on solar requires patience and planning, particularly for extended use.
- Initial Cost: Despite falling significantly (costs have decreased 90% since 2010), the upfront investment for a solar generator can still be substantial, ranging from $500 to $6,000+ for larger systems. This might be a barrier for some budgets, even with the long-term savings.
- Power Output Limitations: While impressive, most portable solar generators cannot match the continuous, high-surge power output of large gas generators. If your primary need is to run heavy-duty construction equipment or a whole-house central AC unit, a portable solar generator might struggle or simply not have the capacity. Large whole-home solar systems can, but those are a different category. For example, running a 5000BTU AC unit (500-600W) on a typical portable unit might only yield 3-6 hours of runtime.
Diving Deeper: Understanding Battery Types
The battery is the heart of your solar generator, and its type significantly impacts performance, lifespan, and safety. While lead-acid batteries were once common, the market has largely shifted to more advanced lithium chemistries.
- Lithium-Ion (Li-ion): These batteries are widely used in consumer electronics and many portable power stations.
- Pros: High energy density (meaning more power in a smaller, lighter package), relatively fast charging, and a good balance of cost and performance. They typically offer 2,000-3,000 charge cycles before significant degradation.
- Cons: Generally more expensive than lead-acid, can be sensitive to extreme temperatures, and carry a very small, but present, risk of thermal runaway (overheating leading to fire) if severely damaged or improperly manufactured.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4): This is the gold standard for modern solar generators and is quickly becoming the dominant battery type.
- Pros: Exceptional safety (virtually no risk of thermal runaway), outstanding longevity (3,000-6,000+ charge cycles to 80% capacity), stable performance across a wider temperature range, and a very long operational lifespan (often 10+ years). These benefits are precisely why more consumers are looking into the benefits of LiFePO4 batteries.
- Cons: Highest upfront cost among battery types and slightly lower energy density compared to some other Li-ion variants (meaning a slightly larger/heavier battery for the same capacity, though still far lighter than lead-acid).
- Lead-Acid (AGM/Gel): Less common in newer portable solar generators, but still found in some older or very budget-friendly models, or as external battery bank options.
- Pros: Lowest initial cost, well-proven technology, and largely recyclable.
- Cons: Very heavy, significantly shorter lifespan (typically 500-800 charge cycles), require more maintenance (though sealed AGM/Gel batteries are less demanding), and suffer from poor cold-weather performance.
For 2025 and beyond, LiFePO4 batteries offer the best overall value for solar generators due to their superior safety, impressive longevity, and reliable performance, making them a wise long-term investment.
Real-World Power: Common Applications for Solar Generators
Solar generators aren't just for emergencies; they're incredibly versatile tools that enhance convenience and independence in a wide array of scenarios.
- Home Backup Power: When the grid goes down, a solar generator can be a lifeline. A 2000Wh unit, for example, can keep a standard refrigerator (drawing around 400W) running for 72+ hours, ensuring your food stays fresh. Beyond that, it can power essential LED lights, your WiFi router to stay connected, charge phones, and critically, keep vital medical devices like CPAP machines operational. This is an essential aspect of essential guide to emergency home power.
- Camping & Outdoor Recreation: Embrace the great outdoors without disconnecting entirely. Solar generators are perfect for powering 12V coolers (saving you from endless ice runs), charging all your devices, running festive LED camp lighting, and keeping portable fans or air pumps going for inflatable beds.
- RV & Van Life: For those living or traveling in an RV or van, a solar generator offers unparalleled freedom. Power your 12V DC fridge, run ventilation fans, keep laptops charged for remote work, and even handle small air conditioners or coffee makers. They're a game-changer for off-grid living and provide vital power solutions for RV and camping.
- Construction & Remote Work Sites: Say goodbye to noisy, smelly gas generators on job sites. Solar generators provide clean, quiet power for charging cordless tool batteries, running LED work lights, operating small power tools, and keeping sensitive electronics like laptops or surveying equipment powered up.
- Emergency Preparedness: Beyond home backup, solar generators are crucial for broader emergency scenarios. They ensure continuous power for medical devices, maintain critical communication systems, help with food preservation during prolonged outages, and provide essential lighting and safety equipment power when other sources fail.
Choosing Your Power Partner: How to Select the Right Solar Generator
With so many options on the market, selecting the perfect solar generator can feel daunting. By breaking down your needs and understanding the key specifications, you can confidently choose a system that truly serves you.
- Assess Your Power Needs: What Do You Want to Run?
This is the most critical step. Make a list of all the devices and appliances you intend to power, noting their wattage (W) and how many hours (h) you'll use them per day.
- Calculation: (Device Wattage × Hours Used) = Daily Watt-hours (Wh)
- Example:
- Refrigerator: 400W × 24h = 9600Wh
- LED Lights: 60W × 6h = 360Wh
- Phone Charging: 20W × 4h = 80Wh
- Total Daily Needs: 10,040Wh
- Determine Capacity Requirements: How Much Storage Do You Need?
Once you have your total daily Wh, you'll need a generator with sufficient battery capacity.
- Factor in Losses: Batteries and inverters aren't 100% efficient. Account for 10-15% battery efficiency loss and 5-10% inverter loss.
- Add a Reserve: Always aim for 20-30% more capacity than your calculated daily needs to provide a buffer for cloudy days, unexpected longer use, or simply peace of mind.
- For our example (10,040Wh daily need): You'd likely need a generator with a usable capacity of at least 12,000-13,000Wh (12-13kWh) to confidently power those items for a full day, assuming you can fully recharge it daily. If you need multiple days of backup without recharging, you'd multiply this capacity by the number of days.
- Consider Portability: Where Will You Use It?
The physical size and weight of the generator are crucial, especially if you plan to move it frequently.
- Ultra-portable: Under 15 lbs (e.g., small camping units).
- Portable: 15-50 lbs (suitable for car camping, RVs, easy lifting).
- Semi-portable: 50-100 lbs (often for home backup, usually with wheels).
- Stationary: 100+ lbs (for permanent installations, not meant for frequent movement).
- Set Your Budget (2025 Prices):
Solar generator prices vary widely based on capacity, output, and battery chemistry.
- Entry-level (200-500Wh): $200-$600 (approx. $0.80-$1.20/Wh) – great for basic charging and small electronics.
- Mid-range (1000-2000Wh): $800-$2000 (approx. $0.60-$1.00/Wh) – good for camping, RVs, and essential home backup.
- High-capacity (3000Wh+): $2500-$6000+ (approx. $0.50-$0.80/Wh) – for extended home backup and heavier loads.
Remember, this is the initial investment; factor in the long-term savings.
- Research Brand Reliability:
Not all solar generators are created equal. Focus on reputable brands known for quality, durability, and customer support. Top brands in the market include Jackery, EcoFlow, Goal Zero, and Bluetti. Reading reviews and comparing models within these brands will help you narrow down your choices. - Evaluate Warranty & Support:
A solar generator is a significant investment, so robust after-sales support is critical. Look for:
- A minimum 2-year warranty (many LiFePO4 units offer 5+ years).
- Clear return policies.
- Accessible customer support (preferably US-based).
- Availability of replacement parts and repair services.
By carefully working through these steps, you'll be well-equipped to select a solar generator that provides reliable, clean power for years to come.
Your Burning Questions Answered: Solar Generator FAQs
As you consider bringing a solar generator into your life, you're bound to have questions. Here are some of the most common ones, answered concisely.
How long do solar generators last?
Quality LiFePO4 units typically last 10-15 years, maintaining at least 80% of their original capacity after 3,000-5,000+ charge cycles. Lithium-ion units usually offer 2,000-3,000 cycles.
Can I use a solar generator in winter?
Yes, but expect 10-25% less efficiency due to shorter daylight hours and lower sun angles. While cold temperatures can actually improve solar panel efficiency, snow accumulation can block panels, significantly reducing or stopping power collection.
Can a solar generator run an AC unit?
Some large-capacity solar generators can run small AC units. A typical 5000BTU window AC unit draws 500-600W. This would limit the runtime to 3-6 hours on most portable units, highlighting the need for careful capacity planning for high-wattage appliances.
What kind of maintenance do solar generators require?
Minimal maintenance is needed. Regularly clean your solar panels to remove dirt or debris, store the generator in a temperature-controlled environment, give it a full charge monthly if unused for extended periods, and annually check all connections for wear.
Is it safe to use a solar generator indoors?
Absolutely. Solar generators produce zero emissions, meaning there's no risk of carbon monoxide poisoning or other dangerous fumes. They are perfectly safe for indoor use, making them ideal for home backup during outages.
Embracing a Brighter, Quieter Future
The evolution of the solar generator marks a pivotal moment in our approach to portable and backup power. From the serene hum of a campsite at night to the reassuring glow of lights during a power outage, these systems offer a future that's cleaner, quieter, and more independent. You now have the foundational knowledge of solar generator basics and how they work, empowering you to make informed decisions for your energy needs.
Whether you're an outdoor adventurer, a remote worker, or simply preparing for life's unexpected moments, a solar generator offers a powerful blend of innovation and sustainability. It's not just about having power; it's about having reliable, emission-free power, on your terms. The sun is shining, and your power is waiting.